
Organic
and inorganic chemistry
Step I. Answer the questions
Ø What do you know
about organic chemistry? What does it study?
Ø What do you know
about inorganic chemistry? What does it study?
Ø Do properties of
organic compounds differ from inorganic compounds?
Step II. Find in the text
sentences with the following word combinations and try to guess their meaning:
Ø beneficial in the treatment; crystalline active
substance; in the terms of the molecular terms; industrial uses; existence of chains.
Text
The
Chemistry of Carbon and Silicon
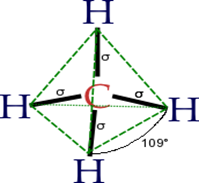 Organic
chemistry is the chemistry of the compounds of carbon. Organic
chemistry is a scientific study of the structure, properties,
and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms
that contain carbon atoms.
Organic
chemistry is the chemistry of the compounds of carbon. Organic
chemistry is a scientific study of the structure, properties,
and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms
that contain carbon atoms.
There are two
principal ways in which organic chemists work. One of these ways is to begin
the investigation of some natural material, such as a plant, which has some
special properties. This plant might, for example, have been found to be
beneficial in the treatment of malaria. The chemist makes an extract from the
plant, and divides the extract into fractions. After each fractionation a study
is made to see which fraction still contains the active substance. Finally this
process may be carried so far that a pure, crystalline active substance is
obtained. The chemist then analyzes the substance, and determines its molecular
weight. Then he investigates the chemical properties of the substance. When the
structure has been determined, he attempts to synthesize the substance; if he
is successful, the active material may be made available in large quantity and
at low cost.
 The
other way in which organic chemists work involves the synthesis and study of a
large number of organic compounds. The ultimate goal of this branch of organic
chemistry is the complete understanding of the physical and chemical properties,
and also the physiological properties of substances in terms of their
molecular structure.
The
other way in which organic chemists work involves the synthesis and study of a
large number of organic compounds. The ultimate goal of this branch of organic
chemistry is the complete understanding of the physical and chemical properties,
and also the physiological properties of substances in terms of their
molecular structure.
Silicon plays an important part in
inorganic world, similar to that played by carbon in organic world. Most of the
rocks that constitute the earth's crust are composed of the silicate minerals,
of which silicon is the most important elementary constituent. Silicon is a chemical element, which has the symbol Si
and atomic number 14. It is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon.
Silicon rarely
occurs as the pure free element in nature. It is more widely distributed in
dusts, sands.
Silicon has many
industrial uses. It is the principal component of most semiconductor devices because it
remains a semiconductor at higher temperatures than the semiconductor germanium. In the form of silica and silicates, silicon forms useful glasses, cements, and ceramics. It is also a
constituent of silicones.
The importance
of carbon in organic chemistry results from its ability to form carbon—carbon
bonds, permitting complex molecules, with the most varied properties, to exist.
The importance of silicon in the inorganic world results from a different
property of the element. The characteristic feature of the silicate minerals is
the existence of chains and more complex structures in which the silicon atoms
are not bonded directly to one another but are
connected by oxygen atoms.
Topical vocabulary:
beneficial – полезный; cement [sə'ment] – цемент; constituent [kən'stɪtjuənt] – компонент, составная часть; crystalline
['krɪst(ə)laɪn] – кристаллический; fractionation
– фракционирование; investigate исследовать, investigation – исследование; malaria [mə'leərɪə] – малярия; molecular
[mə'lekjulə] – молекулярный; semiconductor – полупроводник; silica ['sɪlɪkə] кремнезём; кварц; диоксид кремния; silicate ['sɪlɪkeɪt] – силикат; silicon ['sɪlɪkən] – кремний; silicone [ʹsılıkəun]
– силикон; treatment – лечение; ultimate ['ʌltɪmət] – конечный, окончательный.
Step III.
Translate the following word combinations from English into Russian.
Begin the investigation ______________________________________
Synthesize the substance ____________________________________
Available in large quantity ___________________________________
Ultimate goal ______________________________________________
Complete understanding ______________________________________
Important elementary constituent_______________________________
Widely Distributed_________________________________________________
Silica and
silicates__________________________________________
Characteristic feature_________________________________________
Step IV. Translate the following Russian
word combinations into English:
научное изучение, два основных направления, исследование некоторых
природных материалов, особые свойства, анализировать вещество, синтез и изучение большого количества
органических соединений, силикатные минералы,
полупроводниковые устройства.
Step V. Match two halves of
the sentences.
|
1. Organic chemistry deals with … |
a. … to see which fraction still contain active
substance. |
|
2. One of these ways is to begin investigation… |
b. … its ability to form
carbon—carbon bonds, permitting complex
molecules, with the most varied properties, to exist. |
|
3. After each fractionation a study is made … |
c. … that played by carbon inorganic world. |
|
4. When the structure has been determined… |
d. … structure, properties and reactions of organic
compounds. |
|
5. The ultimate goal of organic chemistry is … |
e. … the characteristic feature of the
silicate minerals, namely, the existence of chains and more complex
structures in which the silicon atoms are not bonded directly to one another but are connected by
oxygen atoms. |
|
6. Silicon plays an important similar to … |
f. … for example, plant which has some special
properties. |
|
7. The importance of
carbon in organic chemistry results from… |
g. … he attempts to synthesize the substance. |
|
8. The importance of silicon in inorganic world results from … |
h. … the complete understanding of physical,
chemical and physiological properties of substances
in terms of their molecular structure. |
Step VI. Make up diagrams



![]()







![]()
![]()

![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()




Step
VII. True or false?
1. Organic chemistry includes all the chemical
components except the many which are based upon chains of carbon atoms.
2. Inorganic chemistry studies matter in its various
forms that contain carbon atoms.
3. Organic chemists create and explore new uses for
new or exciting organic materials.
4. The work of inorganic chemists is based on
understanding the behavior and analogues for inorganic elements, and how these
materials can be modified, separated or used – often in product applications.
5. Silicon doesn’t play any important part in the inorganic
world.
6. Atomic number of Si is 15.
7. Silicon often occurs as the pure free element in
nature.
8. Silicon is used in many industries.
9. Germanium is used as a principal component of most
semiconductor devices because it remains a semiconductor at higher temperatures
than semiconductor silicon.
Step VШ. Find for every word
synonym and antonym from the box

|
|
Synonym |
Antonym |
|
various |
________different_____ |
_________similar______ |
|
obtain |
____________________ |
_____________________ |
|
involve |
____________________ |
_____________________ |
|
complex |
____________________ |
____________________ |
|
constitute |
____________________ |
_____________________ |
|
reactive |
____________________ |
_____________________ |
|
connected |
____________________ |
_____________________ |
Step IX. Answer
the following questions.
1. What is the
difference between organic chemistry and inorganic chemistry?
2. Are there any similarities between organic
chemistry and inorganic chemistry?
3. What are the ways in which organic chemists work?
4. What is the point of the work of inorganic
chemists?
5. What is the goal of organic chemistry and inorganic
chemistry?
6. What is the chemical analog of carbon that plays an
important part in inorganic world like carbon in organic world?
7. Why is carbon so important in organic world?
8. Why is
silicon important in inorganic world?
Step X. Inorganic
chemists may consider inorganic chemistry the hub of the universe, but organic
chemists will be of quite the opposite opinion. Discuss with your partner which
chemistry is more important: organic or inorganic? Say what you think and find
out if your partner agrees or disagrees with you.
Step XI. Choose
any topic you like and make a short presentation.
v The history of the development of organic chemistry
(inorganic chemistry).
v Modern methods and ways in which organic (inorganic)
chemists work.
v The great scientists working in the field of organic
(inorganic) chemistry.

Fun Time
Organic and
inorganic quiz
1. Which element is present in all organic compounds?
a) carbon;
b) nitrogen;
c) oxygen;
d) phosphorous.
2. Which property is generally characteristic of an organic compound?
a) low melting point;
b) high melting point;
c) soluble in polar solvents;
d) insoluble in nonpolar solvents.
3. Compared to the rate
of inorganic reactions, the rate of organic reactions generally is:
a) slower because organic particles are ions;
b) slower because organic particles contain covalent
bonds;
c) faster because organic particles are ions;
d) faster because organic particles contain covalent
bonds.
4. Which statement explains why the element
carbon forms so many compounds?
a) Carbon atoms combine readily with oxygen.
b) Carbon atoms have very high electronegativity.
c) Carbon readily forms ionic bonds with other carbon
atoms.
d) Carbon readily forms covalent bonds with other
carbon atoms.
5. Which compound is an organic acid?
a) CH3OH;
b) CH3OCH3;
c) CH3COOH;
d) CH3COOCH3.
6. This noble
gas is used in the practice of organic chemistry when reactions need to be kept
dry and out of the atmosphere.
a) helium;
b) xenon;
c) neon;
d) argon.
7. Silicon is a member of the _________ group.
a) semi metal;
b) alkali metal;
c) transition metal;
d) basic metal.
8. What is the appearance of amorphous silicon?
a) silver-white;
b) black crystals;
c) pale yellow crystals;
d) brown powder.
9. How many stable isotope does Silicon have?
a) 0;
b) 1;
c) 2;
d) 3.
10. Silicon is found in which of the following gemstones?
a) ruby;
b) amethyst;
c) diamond;
d) pearl.
11. Silicon expands when it freezes.
a) true;
b) false.
12. Silica is a compound of silicon and which element?
a) carbon;
b) hydrogen;
c) sulfur;
d) oxygen.