
Fundamental
Concepts of Chemistry
Step I. Before
reading the text discuss the following questions:
Ø What do you understand under ‘concepts of chemistry’?
Ø What are basic concepts of chemistry to your mind?
Ø Why do chemists use chemical equations?
Step II. Find in
the text sentences with the following word combinations and try to guess their
meanings.
Ø Positively charged core; building blocks; class of
atoms; occur naturally on Earth; neutral salts.
Step III. Before
reading the text learn some useful information.
How to read chemical formulas
HCl — [eit∫ si: el]
HBr — [eit∫ bi: a:]
H2SO4 — [eit∫ tu: es ou fo:]
CF4 — [si: ef fo:]
Cu2O — [si: ju: tu: ou]
H
![]()
![]()
![]() H
C H CH4: ['si:
'eit∫ 'fo:].
H
C H CH4: ['si:
'eit∫ 'fo:].
![]()
H
How to read chemical equations
CH4 + 2O2→ CO + 2H2O ['si: 'eit∫ 'fɔ: 'plʌs 'tu: 'mɔlikju:lz əv 'ou 'tu: 'givz 'si: 'ou 'plʌs 'tu:'molikju:lz əv 'eit∫ 'tu: 'ou].
H+ + NaHCO3→ Na++ H2CO3→
Na+ + H2O + CO2 ['haidrədʒən 'aiən 'plʌs 'en 'ei 'eit∫ 'si: 'ou 'θri: 'givz
'neitriəm 'aiən 'plʌs 'eit∫ 'tu: 'si: 'ou 'θri: 'givz 'neitriəm
'aiən 'plʌs 'eit∫ 'tu: 'ou 'plʌs 'si: 'ou 'tu:]
4HCl + O2 = 2Cl2 + 2H2O ['fɔ: 'mɔlikju:lz əv 'eit∫ 'si: 'el 'plʌs 'ou 'tu: 'givz 'tu: 'mɔlikju:lz əv 'si: 'el 'tu: 'ənd 'tu: 'mɔlikju:lz əv 'eit∫ 'tu: 'ou]
AcOH ↔ AcO− + H+ ['ei 'si: 'ou 'eit∫ 'fɔ:mz ənd iz 'fɔ:md frəm 'ei 'si: 'ɔksidʒən 'aiən 'plʌs 'haidrədʒən 'aiən].
Text
Fundamental Concepts of Chemistry
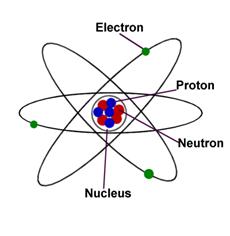 An atom
is a collection of matter
consisting of a positively charged
core, the atomic nucleus, which contains
proton and neutron and which maintains a number of electrons to balance the
positive charge in the nucleus. An atom is also the smallest portion into which an element can be
divided and still retains its properties, made up of a dense, positively charged nucleus surrounded by a system of
electrons.
An atom
is a collection of matter
consisting of a positively charged
core, the atomic nucleus, which contains
proton and neutron and which maintains a number of electrons to balance the
positive charge in the nucleus. An atom is also the smallest portion into which an element can be
divided and still retains its properties, made up of a dense, positively charged nucleus surrounded by a system of
electrons.
The most basic chemical substances are the chemical elements. They are building blocks of
all other substances. An element is a class of atoms which have the same number
of protons in the nucleus. This number is known as the atomic number of the
element. For example, all atoms with 6 protons in their nuclei are atoms of the
chemical element carbon, and all
atoms with 92 protons in their nuclei are atoms of the element uranium. Each chemical element is made
up of only one kind of atom. The atoms of one element differ from those of all other elements. Chemists use letters of
the alphabet as symbols for the elements. In total, 119 elements have been
observed as of 2011, of which 98 occur naturally on Earth. Others have been
produced artificially in nuclear
reactors or in particle accelerator experiments.
An ion is an atom or a molecule that has lost or gained one or more electrons.
Positively charged cation and negatively charged anion can form neutral salts.
Electrical forces at the atomic level create chemical bonds
that join two or more atoms together, forming molecule. Some molecules consist
of atoms of a single element. Oxygen molecules, for example, are made up of two
oxygen atoms. Chemists represent the oxygen by molecule O2. The 2
indicates the number of atoms in the molecule.
When atoms of
two or more of different elements bond together, they form a chemical compound.
Water is a compound made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. The
chemical formula for water is H2O.
Compounds are
formed or broken down by means of chemical reaction. All chemical reactions
involve the formation or destruction of chemical compounds. Chemists use
chemical equation to express what occurs in chemical reactions. Chemical equations consist of chemical formulas
and substances involved in chemical change. For example, the equation C+O2
→ CO2 expresses the chemical change that occurs with one
carbon atom reacts, or bonds, with an oxygen molecule. The reaction produces
one molecule of carbon dioxide, which has the formula CO2.
Topical vocabulary:
accelerator [ək'seləreɪtə] – ускоритель; anion [ʹænaıən]
– анион; artificially [ˌɑːtɪ'fɪʃ(ə)lɪ]
– искусственно; bond – связь; break down
– распадаться, ломать; carbon
– углерод, carbon dioxide [͵kɑ:bən daıʹɔksaıd]
– углекислый газ, диоксид углерода; cation ['kætaɪən]
– катион;
charge – заряд, charged - заряженный; core [kɔː]
– ядро, центр; dense – плотный; destruction [dɪ'strʌkʃ(ə)n] – разрушение, распад; equation [ɪ'kweɪʒ(ə)n] – уравнение; hydrogen
– водород; indicate ['ɪndɪkeɪt] указывать, показывать; ion ['aɪən] – ион; maintain [meɪn'teɪn] – поддерживать, сохранять; molecule
['mɔlɪkjuːl] – молекула; occur [ə'kɜː] – происходить, встречаться, occur
naturally – встречаться в природе; particle
– частица; oxygen – кислород; retain [rɪ'teɪn] – держать, удерживать, сохранять.
Step IV. Find in the text English equivalents to the
Russian word combinations:
скопление
вещества; мельчайшая часть; основные
химические вещества; одинаковое количество протонов в ядре; атомный номер;
атомы элемента урана; встречаются в природе; на атомном уровне; атомы одного
элемента; химические связи; соединения
формируются и распадаются; чтобы показать, что происходит в химических
реакциях.
Step V. Agree or
disagree:
1. Atom is an element, consisting of molecules.
2. Chemical elements are the main chemical substances.
3. Atomic number is a number of elements in a chemical
formula.
4. Chemists use letter of the alphabet as symbols for
the elements.
5. All 119 chemical elements naturally occur on Earth.
6. An ion is an atom or molecule that has lost or
gained one or more electrons.
7. Electrical forces at the atomic level do not create
chemical bonds.
8. Chemists use chemical equation to express what
occurs in chemical reactions.
9. Chemical equations consist of chemical formulas and
symbols that showed the substances involved in chemical change.
10. None of the chemical element has been produced
artificially.
Step VI. Match the words with their
definitions:
|
Atom is… |
an oxide with two atoms of oxygen to one of a metal
or another element
|
|
Molecule is… |
point smth. out |
|
Compound is … |
a subatomic particle with a negative charge, found
in all atoms |
|
Ion is… |
make someone take part in smth. |
|
Oxygen is… |
the smallest particle of a chemical element that can
exist |
|
‘indicate’ means |
a group of atoms forming the smallest unit into
which a substance can be divided |
|
Reaction is … |
a process in which substances interact causing
chemical or physical change |
|
‘involve’ means |
an atom or a molecule with a net electric charge through loss or gain of electrons |
|
Dioxide is … |
a substance formed
from two or more elements
chemically united in fixed proportions |
|
Electron is … |
a colourless, odourless gas that forms about 20%
of the earth’s atmosphere |
Step
VII. There are 10 words, meaning fundamental concepts of chemistry, in the
puzzle. Find them. One is shown for you as an example.

|
A |
T |
X |
R |
A |
M |
D |
V |
E |
J |
|
K |
H |
C |
E |
L |
W |
J |
P |
Q |
H |
|
S |
M |
R |
W |
J |
E |
Y |
R |
U |
A |
|
M |
N |
H |
Q |
S |
R |
X |
O |
A |
S |
|
O |
U |
H |
A |
D |
G |
B |
T |
N |
D |
|
L |
C |
S |
Z |
A |
D |
I |
O |
I |
C |
|
E |
L |
E |
C |
T |
R |
O |
N |
O |
O |
|
C |
E |
A |
A |
O |
N |
N |
H |
N |
M |
|
U |
U |
N |
T |
M |
U |
V |
R |
A |
P |
|
L |
S |
I |
I |
B |
C |
M |
O |
X |
O |
|
E |
V |
O |
O |
S |
V |
Q |
F |
H |
U |
|
R |
F |
N |
N |
E |
U |
T |
R |
O |
N |
|
D |
E |
N |
Z |
F |
N |
Z |
S |
M |
D |
Step
VIII. Answer the following questions:
1. What is atom?
2. What is atom surrounded by?
3. What is chemical element?
4. What is the atomic number of an
element?
5. What does chemical equation consist of?
6.
What is cation?
7. What is anion?
8. What do chemical reactions involve?
9. What is the difference between an element and a compound?
10. Do the atoms of one element differ
from the atoms of all other elements?
Step
IX. Consult your textbooks on chemistry for information about other concepts of
chemistry. What concepts have been
”forgotten” here? Tell your classmates about them.
Step
X. Make a report on some fundamental concept of chemistry.
 Fun Time
Fun Time
Atom Basics Quiz
1. The three basic
components of an atom are:
A. protons,
neutrons, and ions
B. protons,
neutrons, and electrons
C. protons,
neutrinos, and ions
D. protium,
deuterium, and tritium
2. An
element is determined by the number of:
A.
Atoms
B. Electrons
C. Neutrons
D. Protons
3. The
nucleus of an atom consists of:
A. Electrons
B. Neutrons
C. Protons
and neutrons
D. Protons,
neutrons, and electrons
4. A single proton has what electrical charge?
A. No
charge
B. Positive
charge
C. Negative
charge
D. Either
a positive or negative charge
5. Which
particles have approximately the same size and mass as each other?
A. Neutrons
and electrons
B. Electrons
and protons
C. Protons
and neutrons
D. None
- they are all very different in size and mass
6. Which
two particles would be attracted to each other?
A. Electrons
and neutrons
B. Electrons
and protons
C. Protons
and neutrons
D. All
particles are attracted to each other
7. The
atomic number of an atom is:
A.
The number of electrons
B. The
number of neutrons
C. The
number of protons
D. The
number of protons plus the number of neutrons
8.
Changing the number of neutrons of an atom changes its:
A. Isotope
B. Element
C. Ion
D. Charge
9.
When you change the number of electrons on an atom, you produce a
different:
A. Isotope
B. Ion
C. Element
D. Atomic
mass
10. According
to atomic theory, electrons are usually found:
A. In
the atomic nucleus
B. Outside the
nucleus, yet very near it because they are attracted to the protons
C. Outside
the nucleus and often far from it - most of an atom's volume is its electron
cloud
D. Either in the
nucleus or around it - electrons are readily found anywhere in an atom